By: Ashwini Naganthran, Gayathiri Verasoundarapandian and Murni Karim
Article Prepared By: Farah Izana Abdullah
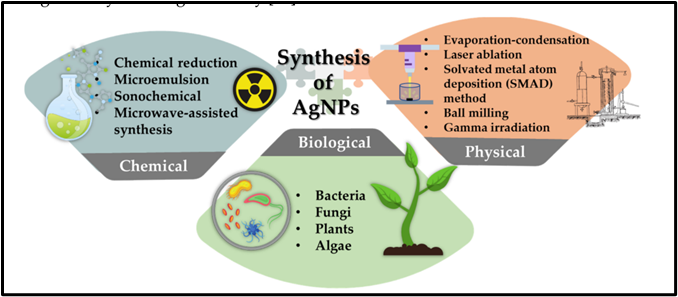
Silver nanoparticles are particles that ranges between 1 to 100 nm. These nanoparticles are unique due to their small size, large surface area to volume ratio, high carrier capacity, high reactivity and easy variation of surface properties. Nanoparticles have been produced through various preparations, including physical, chemical and biological routes. Physical method for synthesis of silver nanoparticles includes evaporation-condensation, laser ablation, solvated metal atom deposition (SMAD) method and ball milling and gamma irradiation. The chemical method is the most conventional way to synthesize silver nanoparticles. The medium of synthesis can be organic or aqueous solvent. Chemical synthesis involves the use of toxic and hazardous chemicals that can be potentially harmful to the environment. These toxic chemicals may be absorbed on the nanoparticles and lead to toxic and adverse effect if used in medical applications. Biological synthesis of silver nanoparticles is the simplest, non-toxic, and yet most eco-friendly method for producing high-quality silver nanoparticles. Biological route synthesis requires living organisms such as bacteria, fungi, plants and algae.
Researchers classified the characterization of nanoparticles they prepared according to their structural, optical, or electrical properties. Nanoparticle structural characterization is further subdivided into morphology, crystal structure, and composition. The application of silver nanoparticles in biomedical applications plays a crucial role contributing to the development of novel antimicrobial agents, biomaterial and medical device coatings, drug delivery formulations, detection and diagnosis platforms, tissue restoration and regeneration materials and performance-enhanced therapeutic alternatives. In addition, silver nanoparticles can be incorporated as additives into membrane, bone cement, denture base, tooth implant, fractured bone, catheters and hydrogel to prevent or reduce formation of biofilm or any medical pathogens as well as improve and fasten the recovery of bone growth, wound and gums recovery.
Web: https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15020427
Date of Input: 30/01/2023 | Updated: 30/01/2023 | m_fakhrulddin
MEDIA SHARING