By: Nicholas Romano, Munirah Ashikin, Jun Chin The, Fadhil Syukri and Ali Karami
Article Prepared By: Farah Izana Abdullah
Microplastics (MPs) may cause harm and may have toxic consequences to aquatic organisms. The detrimental effects of MPs to adsorb pollutants from the environment, and then following ingestion, subsequently release toxic substances into the gut and finally leading to intestinal obstruction. MP fragments in the form of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) were the second most produced globally. Their negative buoyancy facilitates ingestion by bottom dwelling fish such as Barbodes gonionotus and increases their prevalence in ocean sediments.
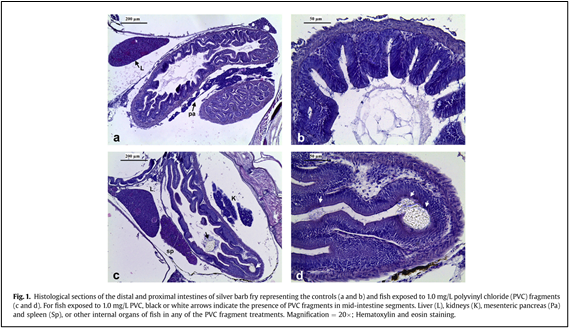
Therefore, short-term effects of PVC fragments on whole-body histology as well as the digestive enzyme trypsin and chymotrypsin activities in B. gonionotus fry was investigated. PVC fragment ingestion was not associated with internal tissue or gill damage, likely due to the smooth surface of the tested PVC fragments and lack of detectable contaminants. However, fish were affected by the presence of ingested PVC fragments, based on intestinal thickening and increased trypsin/ chymotrypsin activities. Further research is urgently needed to better understand to relationship between PVC ingestion and overall health of young fish.
Web: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.11.040
Tarikh Input: 30/08/2021 | Kemaskini: 30/08/2021 | m_fakhrulddin
PERKONGSIAN MEDIA