By: Mohd Hairul Mohd Salleh, Yuzine Esa
Moderated for Web By: Farah Izana binti Abdullah
Oral scrapings and cloacal swabs have been used to recover DNA from living reptiles such as turtles, terrapins, and tortoises. Although whole blood is the ideal supply, numerous blood extraction procedures have been developed. However, Chelonian members vary considerably in their vascular anatomy, degree of cooperation, and the possibility to cause injuries. Blood collection techniques formerly employed on freshwater turtles included highly invasive and fatal operations such as heart puncture and decapitation. Non-lethal and less invasive blood collection methods include venipuncture of prominent veins for example jugular, brachial, femoral, and iliac, the subcarapacial venous plexus, the occipital sinuses, and cardiac puncture.
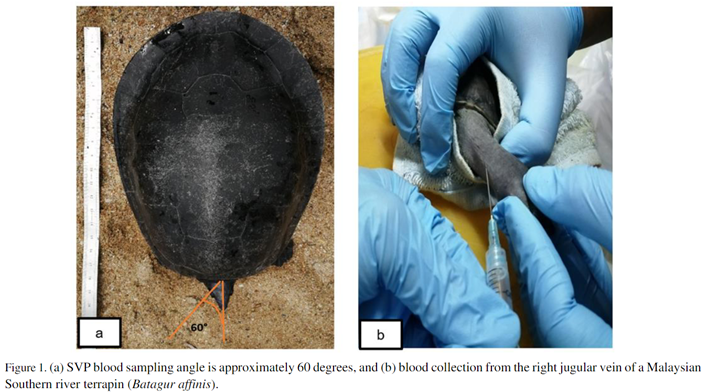
The jugular vein is the blood collection site for Chelonians and should be used whenever possible. In most mammals, the jugular vein is precise and has a lower chance of lymph infection than other locations. The venous contact of the cranial arteries from the azygous veins and the cervical anastomosis of the left and right jugular veins forms the subcarapacial venous plexus (SVP). This blood sampling site is frequently used in uncooperative species where jugular venipuncture without sedation is impossible
From this study, quality of genomic DNA (gDNA) was assessed. As a result, we are the first to provide a complete methods and protocols note on Batagur sp. blood collection. Until the gDNA quality was confirmed, it was the most comprehensive technical discovery from blood draws. The capacity to manage a sample volume without considerable sample contamination solved one of the primary concerns in the field after the invasive approach issue. Moreover, this protocol proved that the blood collection method is advantageous due to its simplicity, rapidity and affordable reagents, apart from the high molecular weight DNA and purity achieved in all samples.
Web: https://ij-aquaticbiology.com/index.php/ijab/article/view/1552/667
Date of Input: 27/04/2023 | Updated: 19/06/2023 | s_humaira
MEDIA SHARING