By: Abd Wahab Farahin, Ikhsan Natrah, Norio Nagao, Fatimah Md. Yusoff, Mohamed Shariff1, Sanjoy Banerjee, Tomoyo Katayama, Masatoshi Nakakuni, Mitsuhiko Koyama, Kiyohiko Nakasaki and Tatsuki Toda
Article Prepared By: Farah Izana Abdullah
There is an increasing demand for microalgae-based products. The global market for microalgae is projected at USD 53.43 billion in the year 2026 as compared to USD 32.60 billion in 2017. These figures show that the microalgae industry is steadily growing and gaining more attention for extensive use in various sectors in the future.
To fulfil the increasing global market demand, research to locate economical sources of nutrients essential to mass culture microalgae is required. Nitrogen, in the form of either ammonium (NH+4) or nitrate (NO−3), is an essential nutrient required for microalgae growth which subsequently contributes to the biomass produced. It is also documented that a certain level of ammonium nitrogen concentration is toxic and can inhibit microalgae productivity.
However, some previous studies had pointed out that different strains of microalgae require different levels of nitrogen uptake. Tetraselmis tetrathele, which belongs to the Chlorophyta phylum, is a green marine microalga widely used in aquaculture as feeds for marine lives, such as molluscs, crustacean larvae and as a probiotic in fish. Chlorophyceae was noted to exhibit significant tolerance to high ammonium nitrogen concentration compared to other algae phyla.
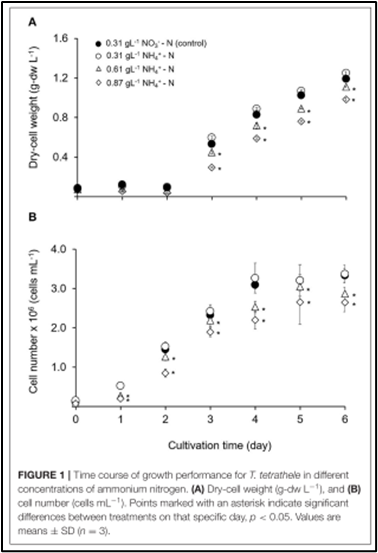
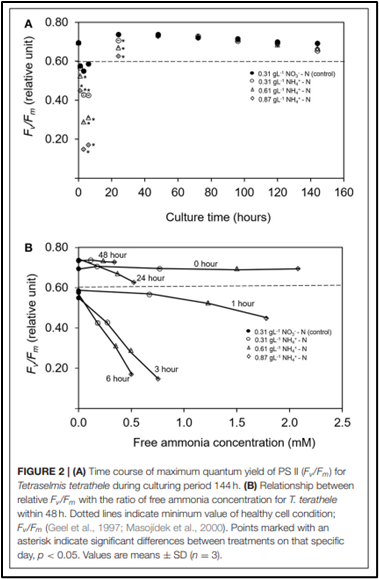
A study has proven that the photosynthetic efficiency of T. tetrathele increased significantly (p < 0.05) in a high concentration of NH+4-N after 24 hours. Chlorophyll a content in T. tetrathele grown in all of the different NH+4-N levels increased significantly. The findings also indicated that T. tetrathele is highly resistant to high ammonium nitrogen which suggests T. tetrathele to be used in the aquaculture industry for bioremediation purposes to remove ammonium nitrogen, thus reducing the production cost while improving the water quality.
Web: doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.568776
Date of Input: 29/06/2022 | Updated: 01/07/2022 | m_fakhrulddin
MEDIA SHARING